Script definitions
To be able to use the Run script access mode with the application behavior rules, you must define the appropriate script types.
This definition tells application control which file accesses it should interpret as script execution.
- Open the context menu of Script definitions.
-
Click New and enter your definition in the following dialog.
The example below defines the Windows Scripting Host.
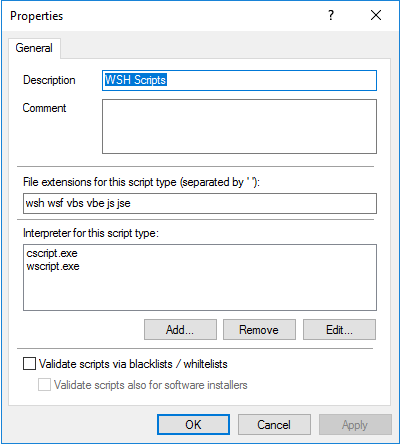
-
Enter the extensions that apply to the script in the File extensions for this script type text box. Simply enter a space between the extensions.
- Enter the interpreters that can interpret your script in the Interpreter for this script type text box.
- With the Validate scripts via blacklists / whitelists option, you can specify to have scripts checked in blacklists or whitelists in the same way as DLLs or EXE files. For more information on blacklisting and whitelisting, see the corresponding chapters.
-
Select the Validate scripts also for software installers option if you want the validation to also apply to scripts started by software update processes.
Example: msiexec.exe is a trusted installer and may only be started if the corresponding MSI file is also trusted.
The Trusted process setting allows you to create a fixed list for such processes.