File properties rule
This rule allows you to specify different file properties to filter by. In addition to some additional options, this rule combines the file owner, file path, hash, and publisher certificate rule options from previous versions.
DriveLock Agents prior to version 2020.2 will only be able to check file properties if the combinations of properties are exactly the same as the settings in the old rule types. For example, if you combine the path with the owner and the publisher, the (old) agent cannot interpret the rule type accurately and will therefore ignore the rule.
Please do the following:
- Path: Start here by selecting a path from which to start (or block) applications, or a specific file within a directory. To do so, click ... . This option checks if the path of the file meets certain conditions.
The other boxes in the dialog will be filled in automatically as soon as you have made a selection here. Then, check the options you want to filter by.
You can also select an application from the list of currently started programs (option From running processes...) or from the application database (option From application inventory...).
To view information about currently running applications from another computer where DriveLock is installed and running via the remote connection, select the on Agent option, enter the name of the computer, and then click Connect.
Also select one of the two options in the drop-down list:
equals: is true if the path corresponds to the specified text, where wildcards can be used. If the text does not contain backslashes, only the file name is checked.
contains: applies if the specified text occurs anywhere in the file path.
- Then assign a rule name and select the rule type, that is, the way the rule will be implemented. For more information, please visit here.
-
Hash: This option verifies that the hash value of the file contents matches the specified value. The system stores this value when creating the rule and compares it with the currently calculated value at runtime. If both match, the rule is activated. Use this option, for example, for a single application that you want to allow or block via whitelist or blacklist.
-
Owner: Use this option to restrict the starting of an application to a specific file owner. For example, you can use this setting to allow all programs installed by an administrator or by a trusted installer account, while blocking all applications that were installed by other users. This also allows for automatically blocking all applications that can be run without prior installation.
The following options can be selected or are entered automatically depending on the selection:
-
Administrators group: This option covers all local administrators. To allow the file, the administrators group must be the explicit file owner.
-
Trusted Installer and Local System: These default Windows accounts must be file owners so that the file is allowed.
-
AD user or group: Select an AD user or group as file owner here. This is where the SID is checked.
-
Name (user / group): You can manually add a user or group here. Here the name is checked.
If you assign a group, the file owner must be the group, not a member of that group.
-
-
Description: Enter the file description here, e.g. 'Paint' for the mspaint.exe file.
-
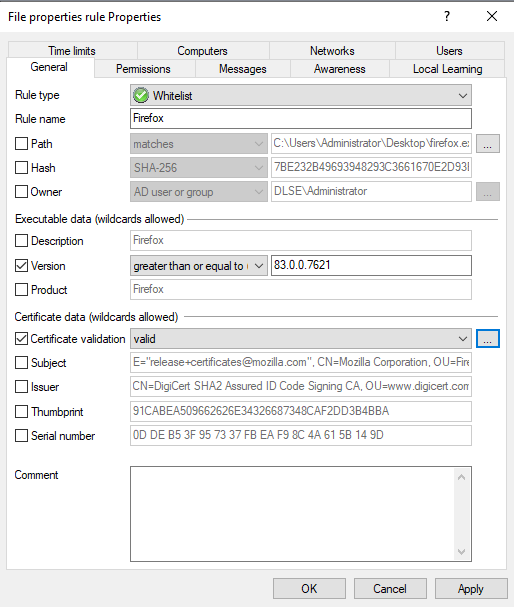
Version: You can have the version checked to prevent users from running other or older program versions, e.g. you can allow Firefox version 83.0.0.7621 or higher and block all previous versions that might contain security vulnerabilities. Select the appropriate option from the drop-down menu, e.g. greater than or equal to.
-
Product: Enter the product name here, e.g. Microsoft Windows operating system.
-
Certificate validation: This option allows you to whitelist signed software or blacklist unsigned software.
You can also use the browse button to select certificates via the application inventory.
Note that Windows files are not signed. You must also enter a file path here, for example.
-
Subject, Issuer, Thumbprint and Serial number are additional certificate properties. The serial number is only unique in combination with the publisher.