Special rule
You can use the special rules to easily identify all program files on a computer that meet a certain criterion, for example, to determine whether a file is part of the Microsoft operating system, or belongs to the installed DriveLock, or is a .NET program. You can also use the special rule to override a blacklist rule, for example, so that some users, such as the service administrators, can run all programs.
Special rules can only be used as whitelist rules.
You can select from the following options in the dialog:
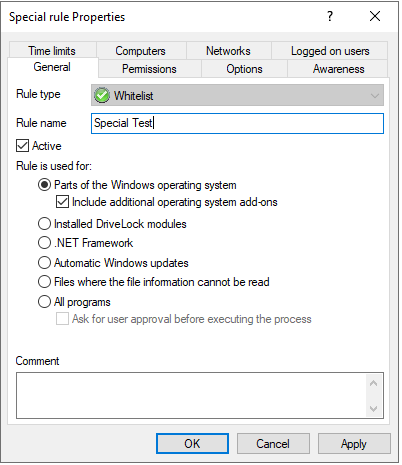
Rule is used for:
-
Parts of the Windows operating system
- includes all programs protected by the Windows System File Protection (WFP)
Include additional operation system add-ons addresses programs in
- C:\windows
- C:\windows\system32
- C:\windows\servicing
- C:\windows\pchealth\helpctr\binaries (Help Center)
- C:\windows\application compatibility scripts
- C:\windows\explorer.exe
- C:\Programs\Internet Explorer
- C:\Programs\Windows Defender
-
Installed DriveLock modules
- Programs in the DriveLock installation directories, for example the DOC Companion Offline Installer. This only includes DriveLock files that have already been installed with administrative rights. This means that users are not allowed to execute any DriveLock files.
-
.NET Framework
- all programs in C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET
-
Automatic Windows updates
- all processes initialized by the Windows Update Agent
-
Files whose information cannot be read
- can be used as a fallback if for any reason DriveLock is not able to access or read information details from a specific file
-
All programs
-
can be used in conjunction with rule limitations for example, to allow access to all programs for the Administrators group, optionally including a user approval before executing the process.
This user permission does not affect the priority of the rule.
-